Prostate Cancer
Overview
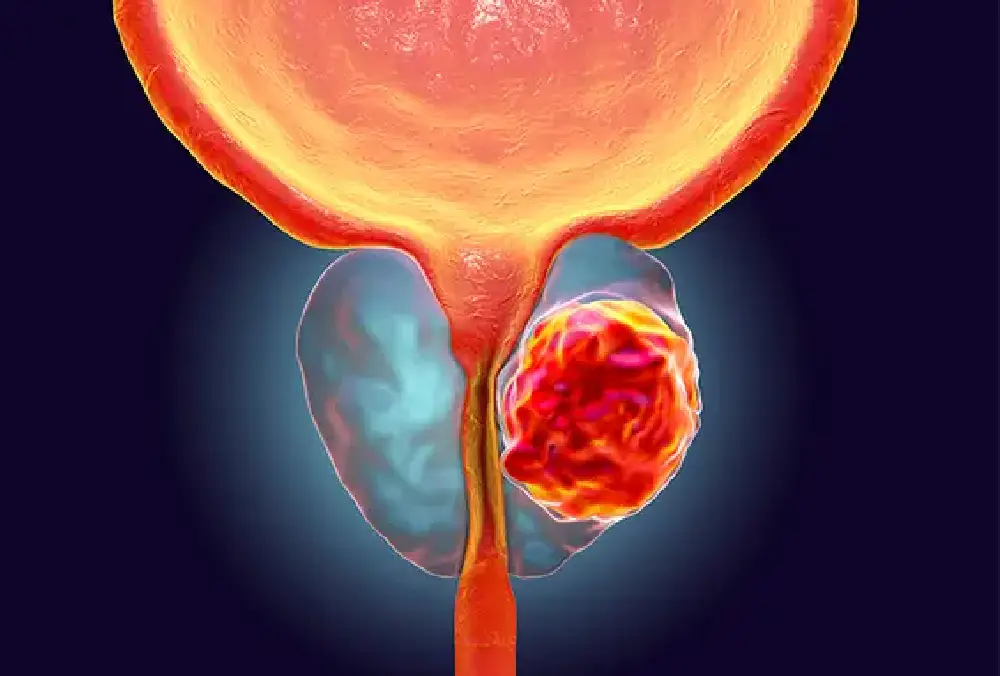
The prostate gland, which generates seminal fluid, is the site of a prevalent cancer in men: prostate cancer. Later stages might result in painful ejaculation, blood in the urine or semen, weak pee stream, frequent urination, trouble beginning, and bone discomfort if it spreads. Early stages typically show no symptoms. In addition to imaging tests like MRIs and CT scans, the diagnosis process usually includes biopsies, digital rectal exams, and PSA blood testing. Active monitoring, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are among the available treatment options. An early diagnosis is essential for efficient care.
What are the types of Prostate Cancer?
Based on the kind of cells it starts in, prostate cancer can be classified. Among the primary kinds are:
Symptoms
Prostate cancer symptoms can vary and include:
Urinating frequently: Especially apparent at night.
Urination difficulty: Having trouble getting the pee to flow.
Weak or interrupted urine stream: A reduction in the urine stream’s intensity or coherence.
Urinary discomfort: Burning or pain during urination.
Anguish during or following ejaculation is known as painful ejaculation.
The inability to obtain or sustain an erection is known as erectile dysfunction.

