Bladder Cancer
Overview
The symptoms of bladder cancer, which commonly include pelvic pain, frequent or painful urination, and blood in the urine, are often caused by cancerous cells lining the bladder. Although squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma are two other types, urothelial carcinoma is the most prevalent type. Chronic bladder inflammation, smoking, and chemical exposure are risk factors. Imaging tests, cystoscopy, and urinalysis are commonly used in the diagnosis process. Radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, surgery, and intravesical therapy are among the available treatment options. Effective illness management requires early detection and treatment.
What are the types of Bladder Cancer?
Based on the cells in which the disease first appears, bladder cancer can be divided into multiple categories. Among the primary kinds are:
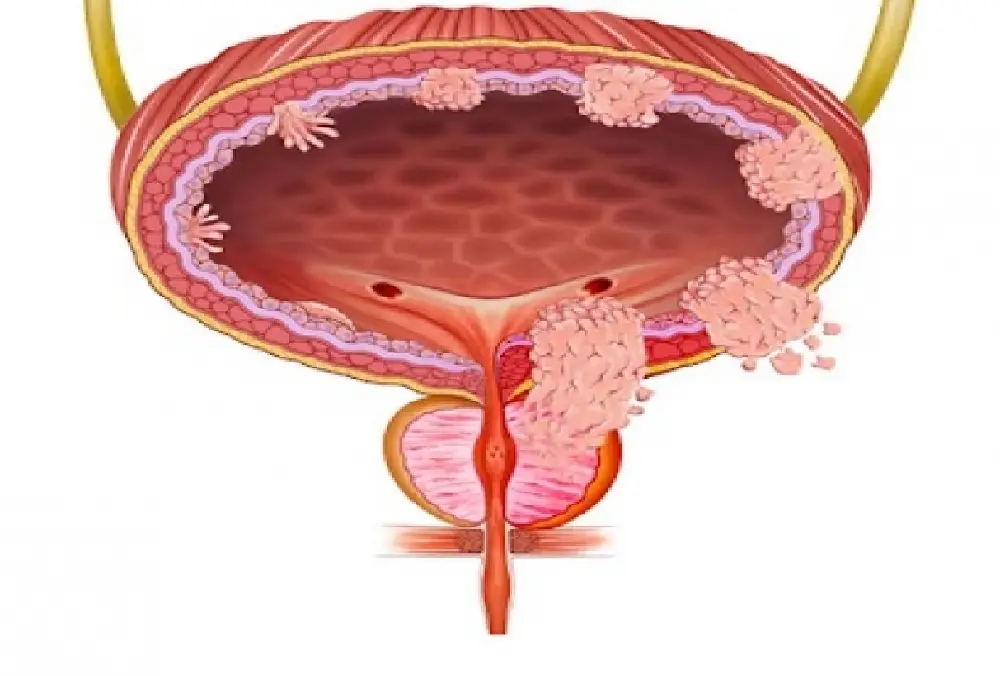
Symptoms
While they can differ, bladder cancer symptoms frequently include:
Blood in the pee (hematuria): Bright crimson or cola-colored urine that can occasionally only be identified through laboratory testing.
Urging yourself more frequently than usual is known as frequent urination.
Urinating that hurts: Experiencing discomfort or a burning feeling.
An intense, enduring need to urinate is called urgency.
Pelvic pain: A ache or discomfort in the lower abdomen.

